lss
lss is a Node.js application with almost the same functionality as GNU coreutils ls plus the following features:
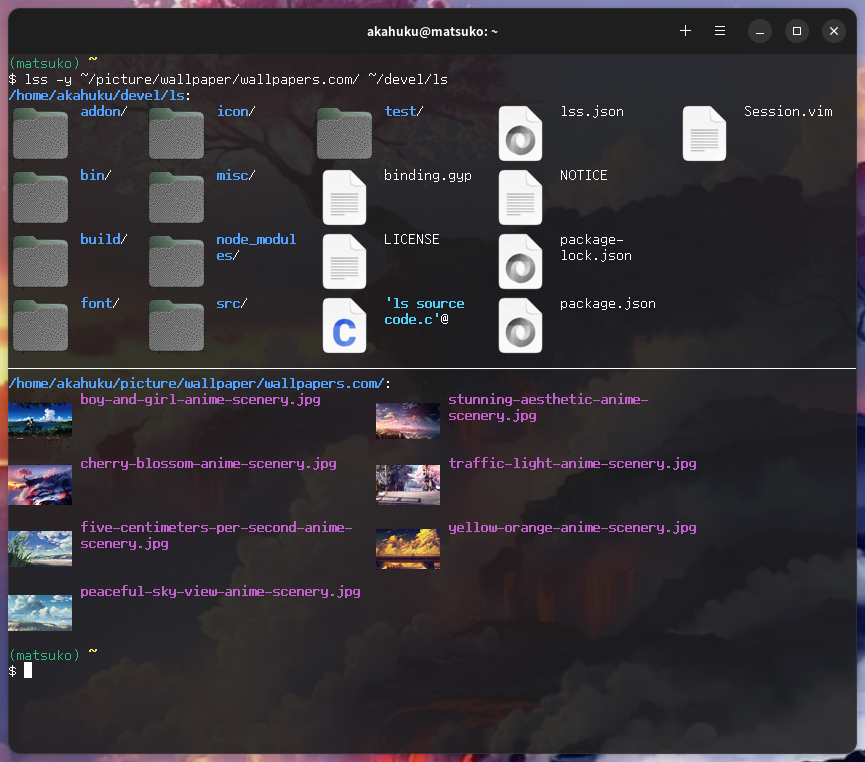
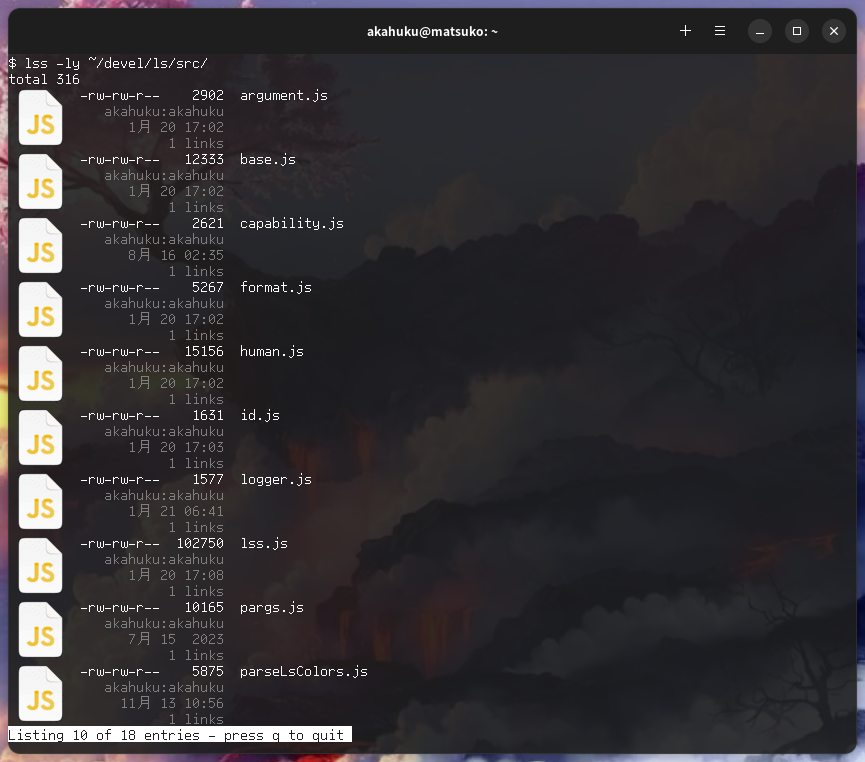
- Displays icons and thumbnails in sixel format
- The icons displayed are equivalent to those displayed by the desktop environment (including theme)
- Displays as many icons as possible, even on systems without a desktop environment installed
- Thumbnails for images, videos, PDFs, fonts, etc. are also generated equivalently using a thumbnailer installed in the desktop environment
- Invokes a pager such as less if the output exceeds the height of the terminal
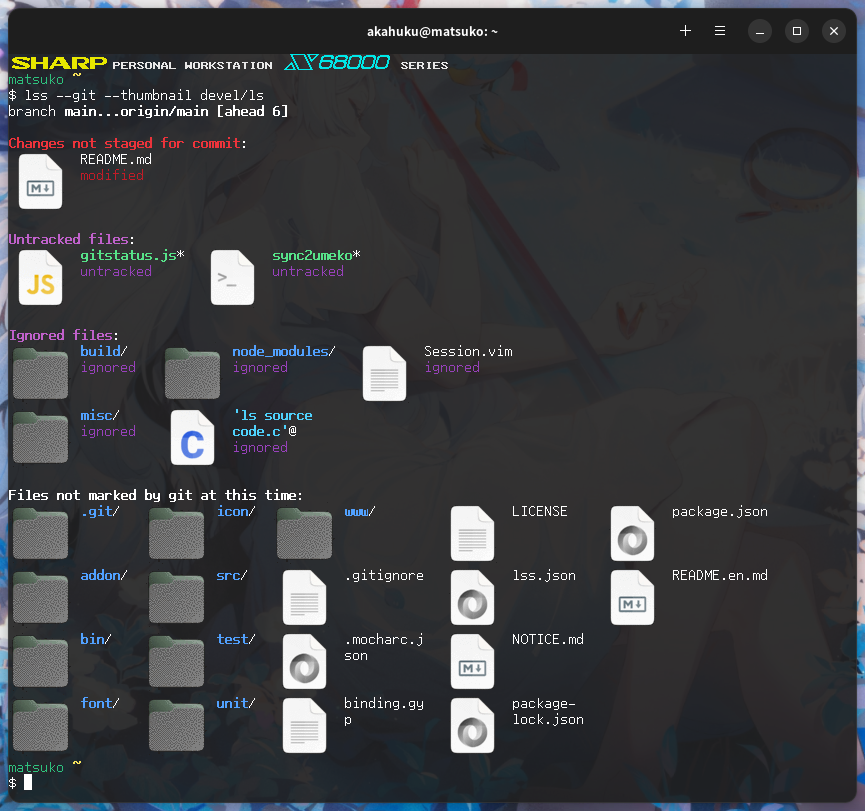
- There is a special display mode if the directory that specified in the argument is a git repository
On the other hand, features that exist in ls but not in lss are as follows:
- Show security context (-Z / --context) - coreutils supports SELinux and smack, but why are other LSMs not supported? I am not sure its reason, so I have not implemented it.
- Special output mode for emacs' dired (-D / --dired) - not implemented as I am not an emacs user
How to install
Environment
lss currently runs on Linux and development and testing is done on Ubuntu. The following example of terminal input and package information assumes Ubuntu (or Debian).
About the thumbnails, I have confirmed their display with the following terminal emulators (or other applications):
Installing lss
First, you need Node.js. v18 or so should work.
Clone the lss git repository to an arbitrary directory
(we will refer to this local repository as <repository>) and install it using npm:
$ git clone https://github.com/akahuku/lss.git
$ cd lss
$ npm installnpm install will install the necessary modules and a systemd timer
to periodically clear the thumbnail caches.
Building the dedicated add-on
The following lss features are not provided in the standard Node.js modules, so lss uses dedicated add-on. If you do not build this add-on, lss will still provide these functions by calling the alternative programs listed in the table, but the performance will not be as good. Therefore, it is recommended to build the add-on along with the installation.
| Function | Alternative Program |
|---|---|
| uid/gid conversion from number to name | getent |
| Obtaining capability information for each file | getcap |
| Obtaining mime types for each file | file |
| Obtaining and setting extended attributes for each file | getfattr / setfattr |
The following programs and development files are required to build the add-on:
| Name | Package |
|---|---|
| gcc | build-essential |
| magic.h | libmagic-dev |
| sys/capability.h | libcap-dev |
Install any packages that are not installed locally.
$ sudo apt install libmagic-dev libcap-devAnd then build:
$ cd <repository>
$ npm run buildPreparation for icon/thumbnail display
The following programs are called internally to display icons and thumbnails:
| Name | Package |
|---|---|
| gsettings | libglib2.0-bin |
| gio | libglib2.0-bin |
| gdk-pixbuf-thumbnailer | libgdk-pixbuf2.0-bin |
| convert | imagemagick |
Install any packages that are not installed locally.
$ sudo apt install imagemagick
:Note that the imagemagick package must be a version that supports sixel output:
$ convert -list format|grep -i sixel
SIX* SIXEL rw- DEC SIXEL Graphics Format
SIXEL* SIXEL rw- DEC SIXEL Graphics FormatMake sure that the 3rd field of the line output by grep has a w.
Usage
<repository>/bin/lss is the executable file.
To run this file from anywhere, add this file path to the PATH environment variable
or place a symbolic link to this file in any path in your PATH.
Basically, the ls usage can be applied directly to lss (except for the -Z / -D / --context / --dired switches). In addition, there are switches unique to lss:
| Switch | Description |
|---|---|
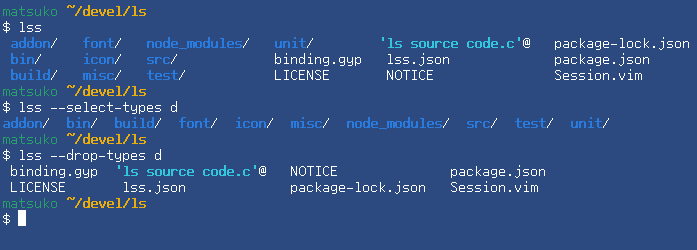
| --drop-types=types | Remove the specified type (see below) from the display |
| --select-types=types | Displays only the specified type (see below) |
| -P, --pager=pager | Specifies the pager name to use when the display exceeds the height of the terminal |
| --git | Turn special display mode on if the directory that specified in the argument is a git repository |
| --header | Displays header lines when used with -l switch |
| -y, --thumbnail | Displays icons and thumbnails when used with -C / -g / -l / -n / -o / -x switches |
| --no-thumbnail | Do not display icons and thumbnails |
| --invalidate-thumbnail-cache | Invalidate the thumbnail cache and force lss to regenerate |
| --collation=method | Specifies the method used to sort file names (not very useful) |
| --diag | Displays terminal capabilities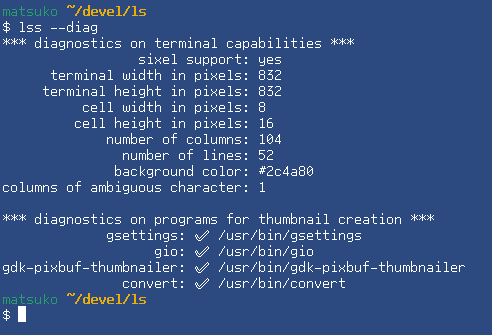 |
| --verbose | Displays detailed information when an error occurs |
lss --help to display all switches.
Types that can be specified for drop-types / select-types
The following strings can be specified, separated by commas. These may be omitted up to single character unless there is ambiguity.
- fifo
- chardev
- blockdev
- directory
- normal | regular
- symbolic_link | link
- sock
- whiteout
Pager names
The following strings can be specified as pager name:
- $PAGER - This string is replaced at runtime by the value of the
PAGERenvironment variable. It is default. - less
- more
- pg
- most
- none | off
Sort methods can be specified for collation
The following strings can be specified for collation:
- intl - Use javascript Intl object. It is default.
- codepoint - Sort by code point in UTF-16 units
- byte - Sort by each byte of UTF-8
TIPS
Define the switches you want to always use
If you define the environment variable LSS_OPTIONS,
lss will act as if its value is prepended to the command line.
It might be good to append
export LSS_OPTIONS="-BF --color=auto --group-directoires-first"to your ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc and so on.
Custom color settings via lss.json
The --color switch allows coloring by escape sequence for each file extension,
and this coloring is based on the environment variable LS_COLORS as in ls.
Other elements are configured in lss.json. Copy <repository>/lss.json to
- If the environment variable
XDG_CONFIG_DIRis set, then$XDG_CONFIG_DIR/lss.json - Otherwise,
~/.config/lss.json
and edit as desired (but not many items can be set yet).
Thumbnail caches
Icons and thumbnails are cached to speed up the second and subsequent output. Caches are placed under
- If the environment variable
XDG_CACHE_HOMEis set, then$XDG_CACHE_HOME/thumbnails/sixel/<terminal-key>/ - Otherwise,
~/.cache/thumbnails/sixel/<terminal-key>/
In this context, terminal-key means <thumbnail height in pixels>-<line height in pixels>-<background color>.
The systemd timer unit lss-prune.timer for maintaining this cache
and the service unit lss-prune.service that actually handles the cache
are placed under ~/.config/systemd/user.
These units are activated once a day and delete caches that are older than 30 days since they were last accessed.
The script that actually maintains the cache is <repository>/bin/prune.
You may call this script directly from the shell.
Difference in sorting method
ls sorts file names by strcoll(), or more precisely, by the method defined by each user's locale. lss, on the other hand, sorts by Intl objects by default. Since these two methods are completely separate, there is no guarantee that the sorting results will be similar.
For example, sorting results may differ for alphabetical case, combined strings with diacritical marks, and characters modified by a variation selector.

License
lss is published under GPL v3 license.
